Needle Bonding
High-Performance, High Through-put Instant Adhesives:
KRYLEX® medical device assembly adhesives have been proven to help manufacturers to improve manufacturing efficiencies and increase reliability and confidence in their finished devices. For disposable medical device assemblies, strong, reliable, sterilization resistant and biocompatible medical liquid adhesives are required for bonding and sealing non-equal materials in various joint geometries.
Needle Bonding Solutions
Hover over the targets to read more information
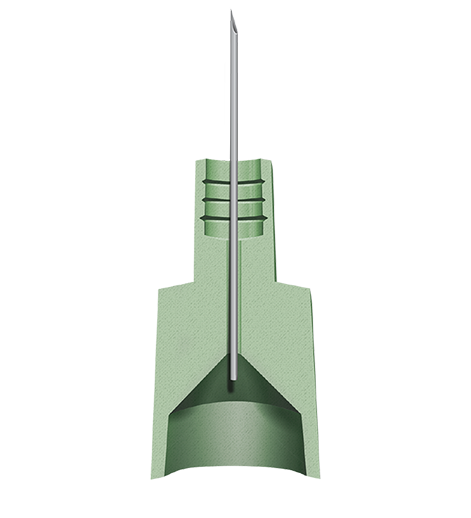 Cannula Gauge
Cannula Gauge
Cannula Gauge
The needle gauge size significantly impacts the assembly pull strength and failure mode. Higher gauges equate to smaller circumference of the cannula and typically result is known pull force. Additionally, because adhesive tend to adhere better to metal than plastic, lower gauge size cannulas tend to display more hub adhesion failure while higher gauge sizes tend to display more cannula adhesion failure.
Engagement Length
The core sits beneath the well where the ID of the hub creates a slip fit with the OD of the cannula. Length of the core is considered the engagement length and typically longer cores relate to higher needle pull strength. It is critical to use lower viscosity adhesives to be able to work in the core.
Hub Material
Hubs can be composed of a variety of plastic substrates. Commonly used materials include ABS, PMMA, PC, PE, PP and PS.
Well Design
Hubs have a well to promote adhesive flow into the core. Wells can be designed to increase needle pull force by making them deeper, increasing the diameter or adding angular rings to provide additional mechanical strength to the assembly. Angular rings are especially popular with low surface energy plastics such as PE & PP.
Cannula Gauge
The needle gauge size significantly impacts the assembly pull strength and failure mode. Higher gauges equate to smaller circumference of the cannula and typically result is known pull force. Additionally, because adhesive tend to adhere better to metal than plastic, lower gauge size cannulas tend to display more hub adhesion failure while higher gauge sizes tend to display more cannula adhesion failure.
Engagement Length
The core sits beneath the well where the ID of the hub creates a slip fit with the OD of the cannula. Length of the core is considered the engagement length and typically longer cores relate to higher needle pull strength. It is critical to use lower viscosity adhesives to be able to work in the core.
Hub Material
Hubs can be composed of a variety of plastic substrates. Commonly used materials include ABS, PMMA, PC, PE, PP and PS.
Well Design
Hubs have a well to promote adhesive flow into the core. Wells can be designed to increase needle pull force by making them deeper, increasing the diameter or adding angular rings to provide additional mechanical strength to the assembly. Angular rings are especially popular with low surface energy plastics such as PE & PP.
Biocompatible, Sterilizable, and Durable
KRYLEX® needle bonding adhesives are ideal for high-speed, high-volume automated syringe assembly lines that incorporate inline testing and packaging. The medical adhesives bond “on-demand” when exposed to LED or UV/Visible light energy.
Solvent-free and single component, medical-grade adhesives also fluoresce for easier inline inspection. These needle bonders adhere to a wide variety of plastics, such as polycarbonate, PA, and PMMA, as well as metal and glass substrates. Applications include:
- Bonding cannulas to hubs
- Hypodermic and biopsy needles
- Syringes
- Winged infusion sets
